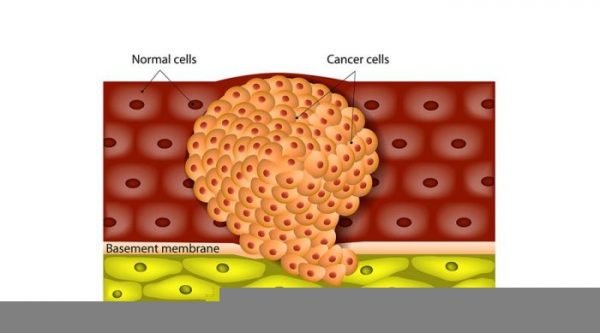
ABOUT BREAST CANCER TREATMENT
Breast cancer treatment varies depending on the stage of the cancer and whether or not the cancer has spread. Cancer occurs when there is an abnormality in cell growth, which causes the cells to divide and grow quickly when the cell should die to make room for new cells.
Breast cancer is the most common type of cancer among women and most often occurs in women over the age of 50, however it can also occur in younger patients. While it is rare, men can also get breast cancer.
Factors which can increase the chances of getting breast cancer include a family history of breast cancer, inherited mutated genes, age, exposure to radiation, and obesity.
Symptoms of breast cancer include a lump in the breast, changes to the skin on the breast, discharge from the nipples, change of appearance of the nipple, and a lump in the armpit. Breast cancer can be detected through regular screening which includes a physical exam, mammogram, breast ultrasound, and breast tissue biopsy.
Once breast cancer has been diagnosed, the doctor will determine the stage of the cancer and whether or not it is metastatic (if it has spread beyond the breasts). This will help the doctor to devise a treatment plan, in many cases, treatments may be combined. Treatments include breast cancer surgery, which is usually a lumpectomy or mastectomy, radiotherapy, chemotherapy, hormone therapy, and targeted drug therapy.
The amount of time that treatment takes varies depending on the type of treatment being performed.
TIME REQUIREMENTS
Average length of stay abroad
The time spent abroad will depend on the treatment. If chemotherapy or radiotherapy are the methods of treatment, then multiple sessions are likely to be required which may mean a longer stay than with surgery.
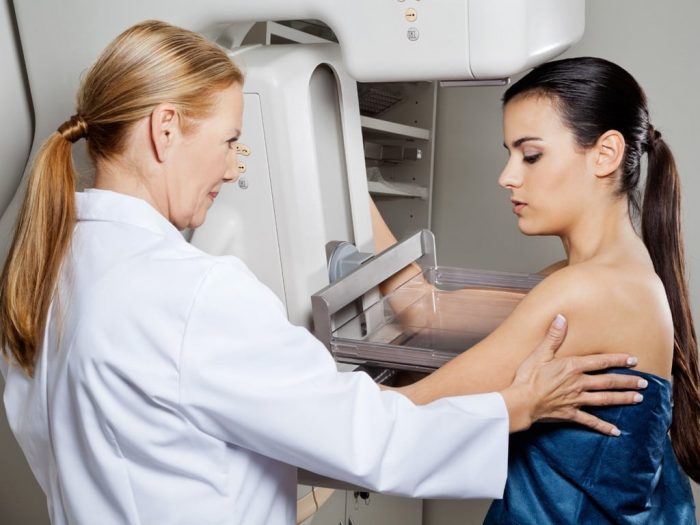
HOW TO FIND QUALITY TREATMENT ABROAD
BEFORE BREAST CANCER TREATMENT ABROAD
Patients should prepare a list of any questions or concerns that they may have, to discuss with the doctor in the consultation before beginning treatment. The doctor will discuss the treatment options and will advise on the best course of treatment. In many cases, treatments may be combined.
If undergoing surgery, patients are usually advised to refrain from eating and drinking in the hours preceding the surgery, in order to prepare for the general anesthetic.
HOW IS IT PERFORMED
Lumpectomy is also known as breast preserving surgery and is usually performed on patients who do not have advanced stages of cancer. The surgeon will make an incision in the breast where the tumor is located and remove the tumor from the breast, as well as part of the breast tissue. Once removed, the incision site is then closed with sutures.
A mastectomy may involve removing the full breast including the skin by creating an incision around the breast. However, if possible, a skin-sparing surgery can be performed, where the nipple is removed but other skin is preserved, and in some cases it is possible to preserve the nipple. Depending on the patient, breast reconstruction surgery may be performed directly after a mastectomy, however some patients may choose to wait and have breast reconstruction as a separate surgery, while others may not choose to have reconstruction surgery.
Chemotherapy is performed by administering dugs intravenously (IV), intra-arterially (IA), or via intraperitoneal (IP) injections to destroy the cancer cells. The treatment is performed over a series of weeks.
Radiotherapy is performed by directing radiation beams at the targeted area, and like chemotherapy, the treatment usually requires multiple sessions which are performed over a series of weeks.
Targeted drug therapy is performed by administering a number of drugs to the patients which will target certain components of the cancer cells. The treatment is usually performed in combination with chemotherapy.
Treatments are most often used in combination with each other, particularly if the cancer is advanced and surgery is being performed. Chemotherapy may often be used before the surgery to shrink the tumor or after the surgery to destroy any cancer that could not be removed during surgery.
Anesthesia
General anesthetic (if surgery is being performed).
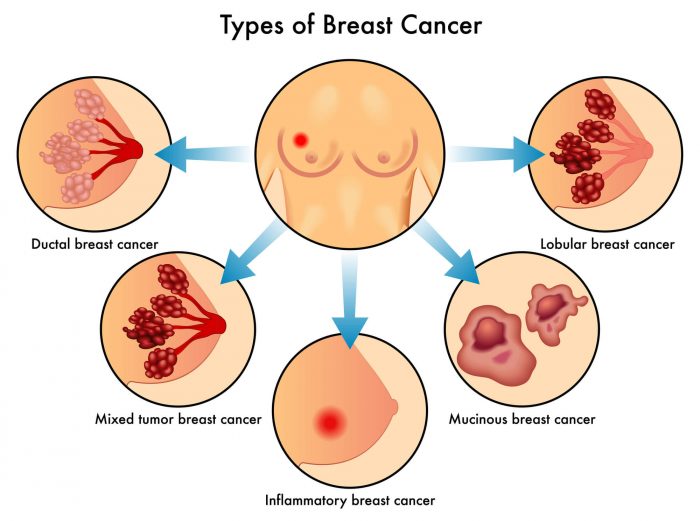
WHAT TO EXPECT AFTER BREAST CANCER TREATMENT
Post procedure care
Most patients need a serious recovery period after a mastectomy, and should plan to spend several weeks recuperating. Most patients will need to take around 2 to 4 weeks off work.
Possible discomfort
Some discomfort is unavoidable after a mastectomy, and patients will be given a set of exercises to keep their arm and shoulders flexible and aid recovery. Patients should expect fatigue, pain and discomfort for at least the first week after the procedure.
IMPORTANT THINGS TO KNOW ABOUT BREAST CANCER TREATMENT
Potential risks
- Infertility (in rare cases)
- Bleeding
- Infection
- Numbness, particularly under the arm
- Shoulder pain and stiffness
Side Effect
- Hair loss
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Mouth sores
- Fatigue