ABOUT OOPHORECTOMY
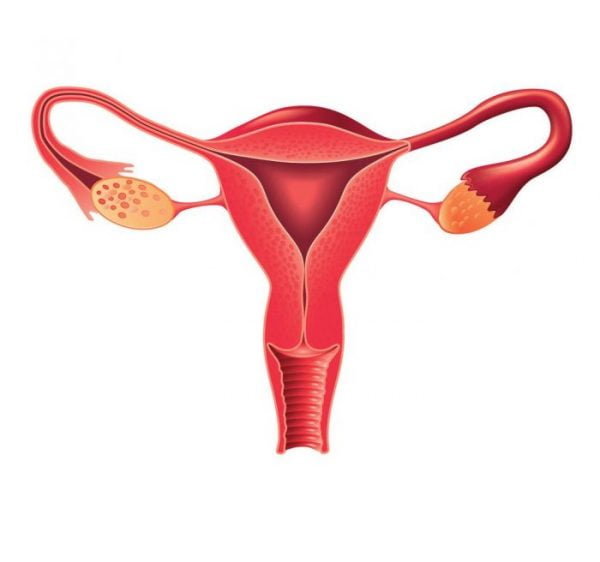
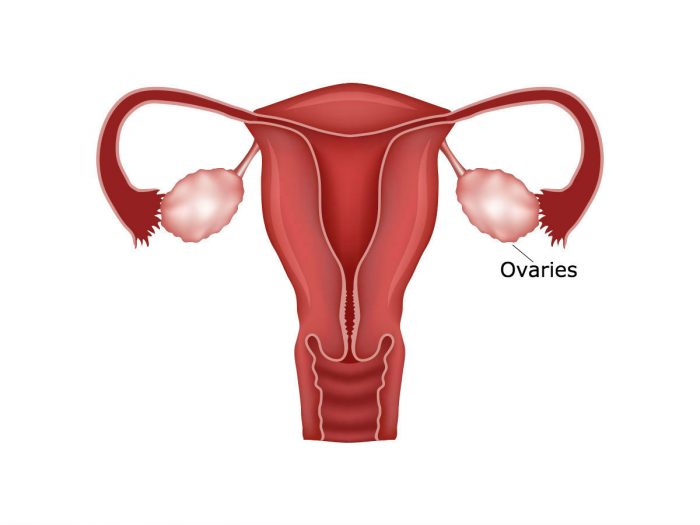
Oophorectomy is a surgical procedure performed to remove one or both of the ovaries. The ovaries are part of the female reproductive system and are located on both sides of uterus, attached to the fallopian tubes. The ovaries are responsible for producing eggs, as well as releasing estrogen and progesterone.
A unilateral oophorectomy refers to the removal of one of the ovaries and a bilateral oophorectomy refers to the removal of both ovaries. If a unilateral oophorectomy is performed, patients will continue to menstruate and can still conceive, however if a bilateral oophorectomy is performed, patients will no longer menstruate or be able to conceive.
The surgery can be performed laparoscopically or as open surgery. The recovery time is quicker after laparoscopic surgery as it is minimally invasive in comparison to open surgery which requires a longer recovery period.
Oophorectomy may be performed in combination with a hysterectomy (removal of the uterus) and salpingectomy (removal of the fallopian tubes). In some cases, an oophorectomy may be performed as a preventive measure in patients who are at high risk of developing ovarian cancer, in such instances, the procedure is referred to as prophylactic oophorectomy.
Recommended for
- Ovarian cancer
- Large ovarian cyst
- Endometriosis
- Certain types of breast cancer
- Reducing risk of cancer in patients with a BRCA genetic mutation
TIME REQUIREMENTS
- Number of days in hospital: 1 – 5 days.
The time spent in the hospital depends on if the procedure is performed laparoscopically or as open surgery.
- Number of trips abroad needed: 1.
COMPARE OOPHORECTOMY PRICES AROUND THE WORLD
HOW TO FIND QUALITY TREATMENT ABROAD
BEFORE OOPHORECTOMY ABROAD
Patients should discuss fertility options ahead of the procedure if undergoing a bilateral oophorectomy. The doctor may request an ultrasound or CT (computerized tomography) scan in order to plan the surgery.
Patients are usually advised to refrain from eating and drinking in the hours preceding the surgery, in order to prepare for the general anesthetic.
HOW IS IT PERFORMED
The surgery is usually performed under a general anesthetic for both laparoscopic and open surgery.
Laparoscopic oophorectomy is performed by making 3 or 4 incisions in the abdomen and inserting a laparoscope through an incision which is fitted with a camera and light. The surgeon will then guide the laparoscope to the ovaries and attach small instruments to the laparoscope via the surrounding incisions. The ovary is then detached and the surrounding blood vessels and the fallopian tubes are tied off. The ovary is then removed in small pieces via the incisions. The incisions are closed with sutures and dressed with a sterile dressing.
Open oophorectomy is performed by making one large incision in the abdomen, either horizontally along the pubic hair line, or vertically extending from the pubic bone to navel. The surgeon will then access the ovaries and separate the ovary from the surrounding blood vessels and fallopian tubes. The ovary is then removed and the incision site is closed with sutures and a sterile dressing is applied.
The patient is then brought to a recovery room until the effects of the general anesthetic have worn off, whereby they will then be brought to the ward. After laparoscopic surgery, the patient may be discharged within one to 2 days. However, after open surgery, the patient will spend more time in hospital, being discharged up to 5 days after the surgery.
Anesthesia
General anesthetic.
Procedure duration
The Oophorectomy takes 1 to 4 hours.
WHAT TO EXPECT AFTER OOPHORECTOMY
Post procedure care
Patients should avoid any strenuous activities and take it easy in the weeks proceeding the surgery. Patients should refrain from having sexual intercourse until the doctor confirms it is ok.
IMPORTANT THINGS TO KNOW ABOUT OOPHORECTOMY
Potential risks
- Bleeding
- Infection
- Adverse reaction to the general anesthetic
- Damage to surrounding organs
- Small bowel rupture