ABOUT CHEMOTHERAPY
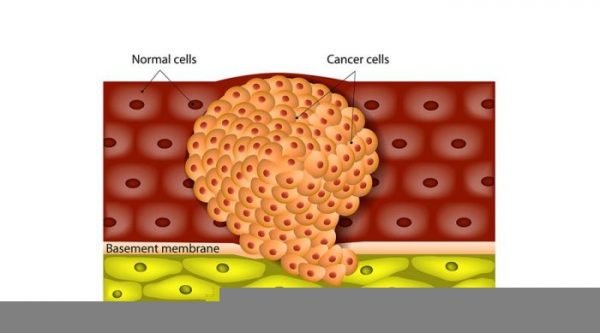
Chemotherapy is the use of medicine or drugs that contain chemical substances to treat cancer. It can be used in combination with other cancer treatments such as radiotherapy or surgery. Chemotherapy works by destroying cancerous cells that quickly develop or multiply.
While chemotherapy is used to destroy or slow down the growth of cancer cells, it can also destroy healthy cells such as those present in hair follicles and bone marrow. This accounts for some of the many side effects of chemotherapy, which include hair loss, fatigue, and nausea. The side effects will usually subside after the treatment is complete.
Depending on the type of cancer being treated, chemotherapy may be able to fully destroy the cancer, control it by stopping the cells from dividing and multiplying, or help to relieve symptoms of cancer. By having chemotherapy before surgery, it can help to reduce the size of the cancer or prevent it from spreading, therefore making it easier to surgically remove the remaining cancer.
During chemotherapy treatment, one particular drug may be used, or the doctor may use a combination of drugs. The treatment is given in cycles, which means it is given over a period of a certain amount of days, and is then followed by a rest period of 3 weeks for example, in order to allow the body to recover and produce new healthy cells before the next cycle. The amount of cycles required depends on the type of cancer being treated, the aim of the treatment, and on the individual patient.
Recommended for
- Treating cancer
- Managing cancer
TIME REQUIREMENTS
- Number of days in hospital: 1.
After receiving chemotherapy, the patient will usually leave the hospital on the same day.
- Average length of stay abroad
The amount of time abroad will depend on how many chemotherapy cycles are required.

HOW TO FIND QUALITY TREATMENT ABROAD
BEFORE CHEMOTHERAPY ABROAD
Before beginning treatment, the patient will meet with the oncologist to discuss the treatment plan. The doctor will advise on the drugs that will be used and on the method of administering the drugs. The oncologist will perform a series of tests to ensure that the patient is healthy enough to have chemotherapy.
If patients plan to have children, the oncologist may refer the patient to an fertility specialist, as having chemotherapy can cause infertility, therefore freezing embryos or sperm can optimize the chances to later conceive a baby.
The oncologist may advise that the patient should makes an appointment with a dentist in order to ensure there are no infections inside the mouth after the chemotherapy, as this can be one of the side effects of treatment.
If the chemotherapy will be administered intravenously, than a central venous catheter (CVC) may be implanted into a large vein in the upper arm before the treatment, in order to aid the transfer of drugs into the body.
Patients should arrange for someone to take them back to the hotel after the treatment as they may feel exhausted and nauseous afterwards.
Patients with complex conditions may benefit from seeking a second opinion before beginning a treatment plan. A second opinion means that another doctor, usually an expert with a lot of experience, will review the patient’s medical history, symptoms, scans, test results, and other important information, in order to provide a diagnosis and treatment plan. When asked, 45% of US residents who received a second opinion said that they had a different diagnosis, prognosis, or treatment plan.
HOW IS IT PERFORMED
There are various methods of administering chemotherapy which include intravenous (IV), intra-arterial (IA), or intraperitoneal (IP) injections. Chemotherapy can also be given orally or applied using topical creams.
Chemotherapy administered intravenously may be delivered via a central venous catheter (CVC) that is implanted before the treatment, a central line in the chest, or directly into a vein through a cannula placed in the hand. A needle, which is connected to a tube that the drugs flow through, is inserted into the CVC, central line, or the cannula to deliver the drugs.
The drugs can be injected into the blood with a needle or can be administered through an artery, which is referred to intra-arterial (IA). Intraperitoneal administration involves administering the drugs through peritoneal cavity which contains the stomach, intestines, and liver.
The drugs can be applied to the skin topically as a cream which is absorbed by the body. The other option is to administer the drugs orally through tablet or liquid form.
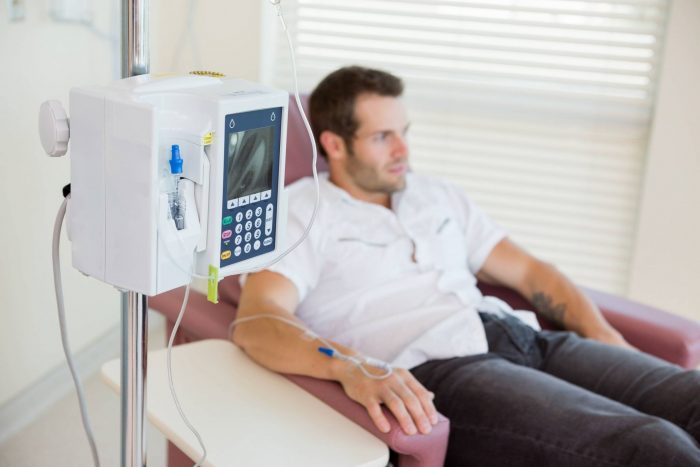
Possible discomfort
Patients may feel nauseous and exhausted after chemotherapy. If they experience a lot of side effects, they should notify the doctor as many of the symptoms can be managed.
IMPORTANT THINGS TO KNOW ABOUT CHEMOTHERAPY
Not recommended for
- Pregnant patients
Potential risks
- Pain
- Infertility
- Heart or kidney problems
- Nerve damage
Side Effect
- Hair loss
- Vomiting
- Nausea
- Fatigue