ABOUT PROSTATECTOMY
A prostatectomy is a surgical procedure which involves removing all or part of the prostate gland. The surgery is performed to treat prostate cancer or to treat conditions such as benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) and prostatitis, which affect the urinary system.
BPH is a condition that is brought on by age and causes the prostate glands to become larger, which in turn, can cause problems with urinating such as having a frequent need to urinate, and experiencing interrupted urinating. Prostatitis is a condition that causes the prostate gland to become inflamed and infected.
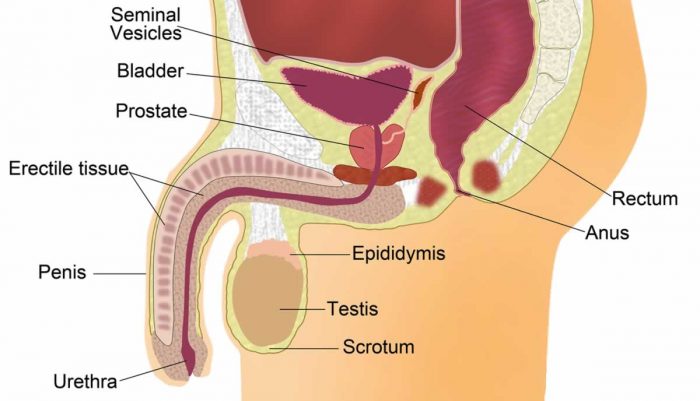
The prostate gland is part of the male anatomy and is located under the urinary bladder. The prostate gland has both a sexual and urinary function, however, its main purpose is to secrete fluid which contains semen.
There are different types of prostatectomies which can be performed, and they are split into 2 different categories, radical prostatectomy and simple prostatectomy. Depending on the surgery, it may be performed laparoscopically or as an open surgery.
A radical prostatectomy is most commonly performed to treat prostate cancer and involves removing all of the prostate glands and some surrounding tissue. A simple prostatectomy is performed to treat conditions which are causing problems with the urinary system or to treat enlarged prostate glands. It involves removing the part of the prostate gland which is restricting the flow of urine.
Recommended for
- Prostate cancer
- Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH)
- Prostatitis
- Prostatism
TIME REQUIREMENTS
- Number of days in hospital: 2 – 4 days.
- Average length of stay abroad: 1 – 3 weeks.

HOW TO FIND QUALITY TREATMENT ABROAD
BEFORE PROSTATECTOMY ABROAD
Before the surgery, the doctor may perform a cystoscopy to examine the bladder, by inserting an endoscope through the urethra. Tests to measure the size of the prostate are also performed.
The doctor will advise what medications need to be stopped ahead of the surgery. Patients will usually need to refrain from eating and drinking in the hours before the surgery, in order to prepare for the general anesthetic.
Patients with complex conditions may benefit from seeking a second opinion before beginning a treatment plan. A second opinion means that another doctor, usually an expert with a lot of experience, will review the patient’s medical history, symptoms, scans, test results, and other important information, in order to provide a diagnosis and treatment plan. When asked, 45% of US residents who received a second opinion said that they had a different diagnosis, prognosis, or treatment plan.
HOW IS IT PERFORMED
There are a number of surgical methods as to how radical prostatectomy is performed. Laparoscopic surgery is one of the surgical options that involves making a number of small incisions in the stomach, through which an endoscope is inserted and used to remove the prostate gland using camera guidance. Laparoscopic surgery can also be performed using robotic assistance, which can make smaller incisions that are more precise, meaning even shorter recovery times.
When performing a prostatectomy, the surgeon may use a nerve-sparing technique in order to spare the nerves surrounding the prostate gland in an effort to preserve the ability to have an erection. This involves cutting around the nerves in order to preserve them and leave them intact. It can be performed in both radical or simple prostatectomy methods.
A simple prostatectomy is performed through open surgery. This type of surgery involves making an incision either in the abdomen, which is referred to as the retropubic approach, or in the perineum, the area between the anus and the scrotum, which is referred to as the perineal approach. The retropubic approach is more commonly used and often involves removing the lymph nodes as well as the prostate gland and can leave the nerves intact. The perineal approach is less frequently used, as the lymph nodes cannot be removed, nor can the nerves be spared.
Anesthesia
General anesthetic.
Procedure duration
The Prostatectomy takes 1 to 2 hours.
WHAT TO EXPECT AFTER PROSTATECTOMY
Post procedure care
A catheter may be left in the bladder to drain urine for 1 to 3 weeks after surgery. Patients can usually leave hospital after a few days, and should get guidance on how to take care of the catheter at home.
Possible discomfort
Some discomfort and soreness is normal and to be expected, further bladder control can be poor for a few months after the catheter is removed.
IMPORTANT THINGS TO KNOW ABOUT PROSTATECTOMY
Success rates
As a treatment for early stage cancer, a prostatectomy is usually effective.
Potential risks
- Infection
- Bleeding
- Urinary tract infection
- Sterility
- Erectile dysfunction
- Urinary incontinence
- Damage to the rectum or urethra