ABOUT EYE EXAMINATION
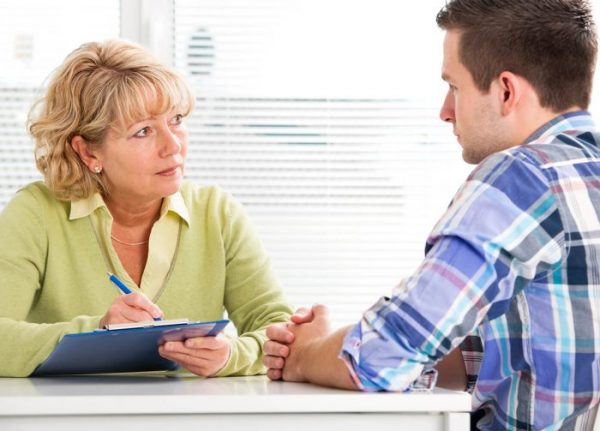
An eye examination is a combination of tests performed on the eyes, in order to determine the health of the eyes and to assess the vision.
Eye examinations may be performed on all components of the eye, including the iris, retina, pupil, optic nerve, retinal blood vessels, cornea, lens, vitreous, and anterior chamber.
The eye examination can be performed by an ophthalmologist, optometrist or an optician.
An eye examination can determine if the patient has problems with their vision and require glasses, or determine if there are any diseases or problems with the eye.
Recommended for
- Patients who are experiencing problems with their vision
- Older patients are particularly more prone to developing glaucoma and cataracts and should have their eyes examined every 1 to 2 years
TIME REQUIREMENTS
- Number of days in hospital: 1.
Patients can usually go home once the eye examination is complete.
- Number of trips abroad needed: 1.

HOW TO FIND QUALITY TREATMENT ABROAD
BEFORE EYE EXAMINATION ABROAD
When booking the appointment, patients may be asked to describe any problems or existing conditions that they may have.
Patients who already wear glasses or contact lenses, should remember to bring them to the appointment. Patients should also bring a pair of sunglasses for after the treatment, as the eyes may be sensitive to light if the pupils have been dilated (enlarged) during the exam.
HOW IS IT PERFORMED
The ophthalmologist will start the examination by first going through the patient’s medical history and asking questions about their vision.
In a vision test, the patient will be asked to look at an eye chart to read the letters on each line. The ophthalmologist will do a cover test which involves covering one of the eyes while asking the patient to look at a small target located far away and then closer, in order to check the movement of the eyes.
In order to examine the pupils, a light is used to check the reaction to light and also to examine the exterior of the eye. For patients who wear prescription glasses or contact lenses, a refraction test will be carried out, and the patient will be asked to look into different lenses to see if the vision improves or worsens.
A biomicroscope is used to shine light into the front of the eye, in order to examine the cornea, lens, and the iris. An ophthalmoscope is used examine the back of the eye.
To test the dilation of the pupil, drops are applied to the eye and this makes the eyes more sensitive to light and may cause blurriness. To assess the thickness of the cornea, an ultrasound is used.
An eye examination may also include intraocular pressure tests (tonometry), visual field tests to test peripheral or “side” vision, or corneal topography – mapping the shape and curvature of the cornea.
After thoroughly examining the eyes, the doctor will then explain the findings to the patient and discuss the next steps if there have been any conditions or problems found.
Procedure duration
The Eye Examination takes 30 to 60 minutes.
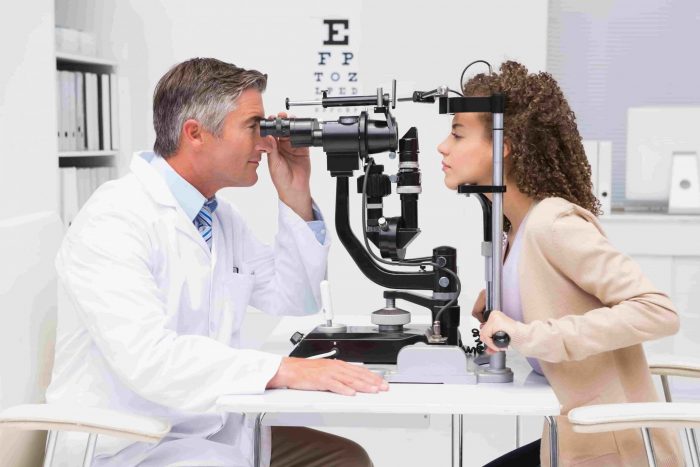
WHAT TO EXPECT AFTER EYE EXAMINATION
Post procedure care
Patients may need to wear sunglasses for a few hours after the eye examination, as the eyes may be sensitive to light after the eye drops have been used to dilate the pupils.
Possible discomfort
Patients may experience blurriness or sensitivity to light for a few hours after the examination.